It is a long-term goal of several enterprises, including PANTHEON.tech, to embrace an open(-source) ecosystem for network development and connectivity.
An open approach to software development opens doors to all the talents around the globe, to contribute to projects that will shape the future of networking. One such project is the Open Radio Access Network or O-RAN for short.
Next In Line: O-RAN
Originally launched as OpenRAN, the project was started in 2017 by the Telecom Infra Project. The goal was to build a vendor-neutral, hardware & software-defined technology for 2-3-4G RAN solutions.
Then, the O-RAN Alliance was founded to increase community engagement, as well as to motivate operators to be included in this development. The alliance has made it a point, to create a standardization – meaning a description, of how this concept should function in reality.
O-RAN Architecture
O-RAN is part of the massive evolution from 4G networks, into the 5G generation. In 5G, due to higher bandwidths, more antenna and the use of multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) technology, even more data needs to go back and forth.
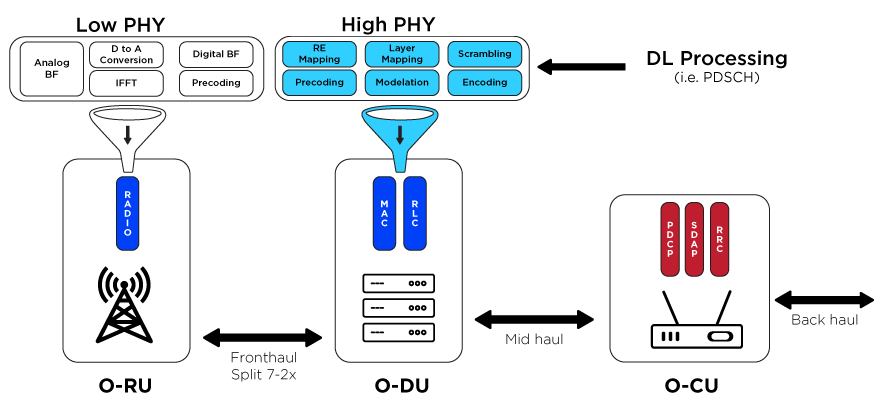
We can observe the formation of two solutions: the high-level split (HLS) and the low-level split (LLS). With so much of the processing shifting to the edge, the high-level split is a two-box solution. The F1 interface lies between the DU+RU and links to the centralized device. Alternatively, further processing is shifted to the middle by LLS and the antenna is held at the edge.
Three separate units are deployed with O-RAN:
- O-RU: Radio Unit
- O-DU: Distributed Unit
- O-CU: Centralized Unit
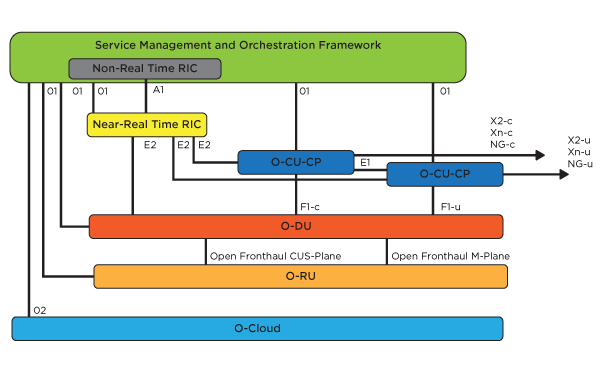
At the edge sits the O-RU. In the center, the O-DU sits and performs some of the processing. Both HLS and LLS are included in O-RAN. They standardize the interfaces. For CUs, DUs, or RUs, operators may use different vendors. With one working group concentrating on the F1 interface and another on the front-haul, the components are much more interoperable and the protocols more clearly defined.
What’s more, O-RAN selected SDN-R as the project’s SDN controller. PANTHEON.tech is part of the SDN-R community.
What is a RAN?
A radio access network implements radio access technology, which makes it able for user devices (anything able to receive this signal) to receive a connection to the core network, above the specific RAN.
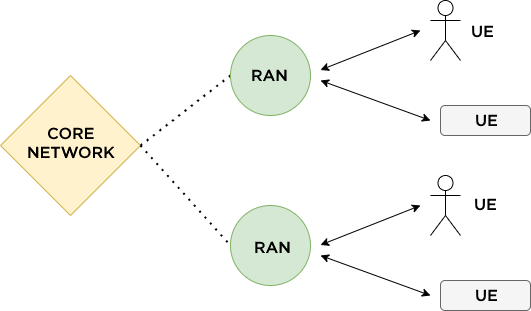
A visual representation of core networks, radio access networks, and user devices.
The types of radio access networks include GSM, EDGE, and LTE standards, named GRAN, GERAN, E-UTRAN in that order.
The core network provides a path for information exchanging between subnetworks or different LANs. Imagine the core network as the backbone of an enterprise’s entire network.
The technology behind RANs is called RAT (radio access technology) and represents the principal technology behind radio-based communication. RATs include known network standards like GSM or LTE, or Bluetooth and WiFi.
Linux Foundation Networking Presents: O-RAN Software Community
In the first half of 2019, The Linux Foundation, in collaboration with the O-RAN Alliance, created the O-RAN Software Community, where members can contribute their knowledge & know-how to the O-RAN project.
Currently, the goal is to create a common O-RAN specification, that all RAN vendors would potentially adopt. This would mean a common interface, independent of the radio unit type.
This move certainly makes sense, since, at its core, O-RAN stands for openness – open-source, nonproprietary radio access networks. As the technical charter of the project puts it:
The mission of the Project is to develop open-source software enabling modular open, intelligent, efficient, and agile radio access networks, aligned with the architecture specified by O-RAN Alliance.
The further goal of creating a software community centered around this project is to include projects such as OPNFV, ONAP, and others, to create a complete package for future, open networking.



![[Release] lighty.io 22.1.0](https://pantheontech1.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/lighty-22.1-400x250.jpg)
![[Release] OpenDaylight Titanium](https://pantheontech1.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/odl-titanium-release.png)
![[Meet Us] PANTHEON.tech @ Open Source Summit 2025 in Amsterdam](https://pantheontech1.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/OSS_Temp.png)